table of contents
RBI Models
The AsInt software solution is agnostic to the RBI (Risk Based Inspection) methodologies. We have worked hard to “templatize” various methodologies.
This approach allows customers to choose from an existing list within our library, or BYORM (Bring Your Own Risk Model). This could be the:
RBI+ Model - AsInts own model based on the API 5813rd Damage Mechanisms and the NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) fluid list for consequences.
API 5813rd
European PED (Pressure Equipment Directive)
Brazilian NR13
Your own model
Risk Matrix Options
There are no limitations to the risk matrix options, other than the restriction is currently 2D (X and Y axis), though you can have an infinite number or X and Y axis options per matrix. Below are some examples of risk matrix options.
Some are whimsical to show the power of flexibility, others are realistic.
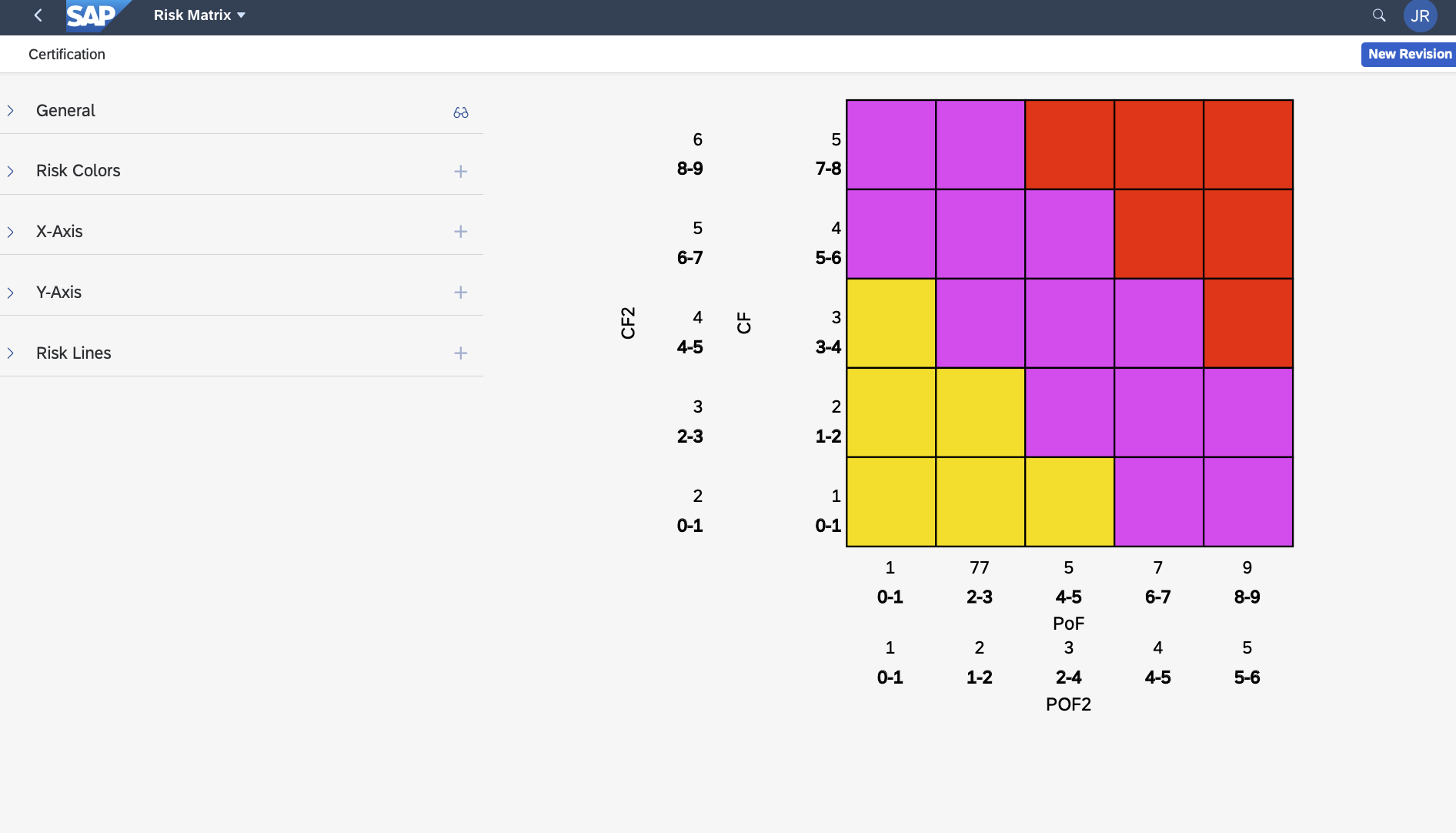
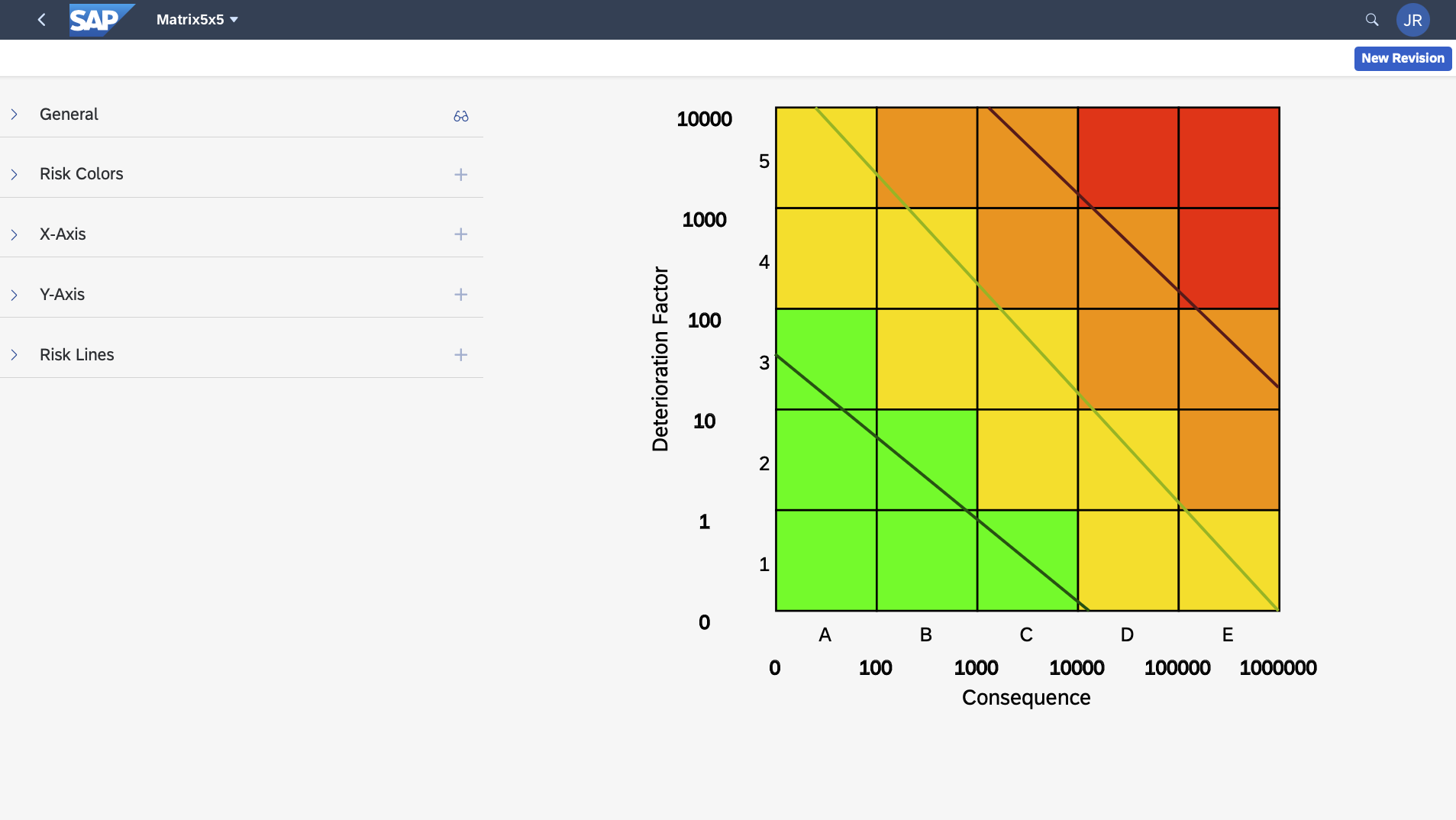
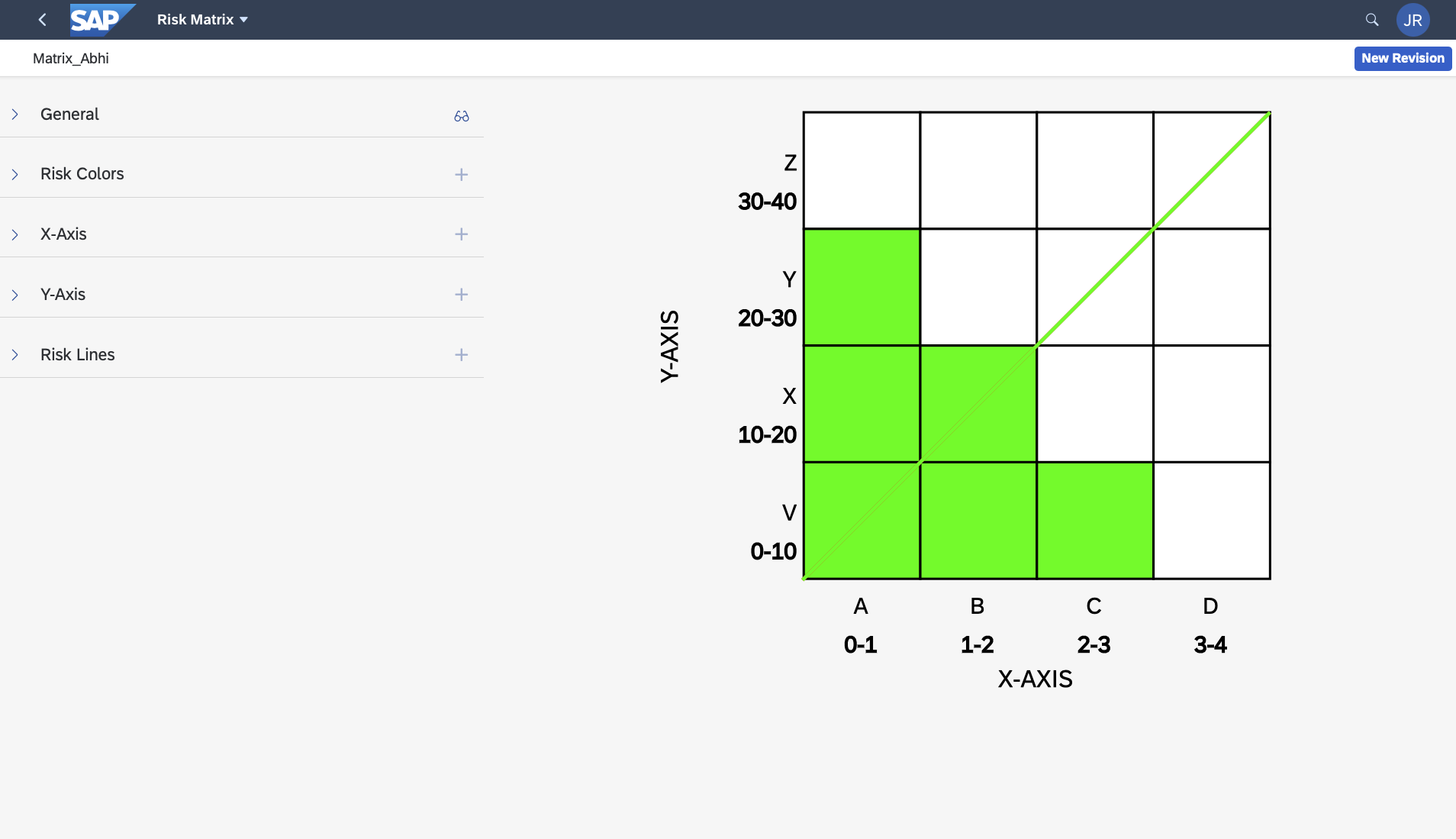
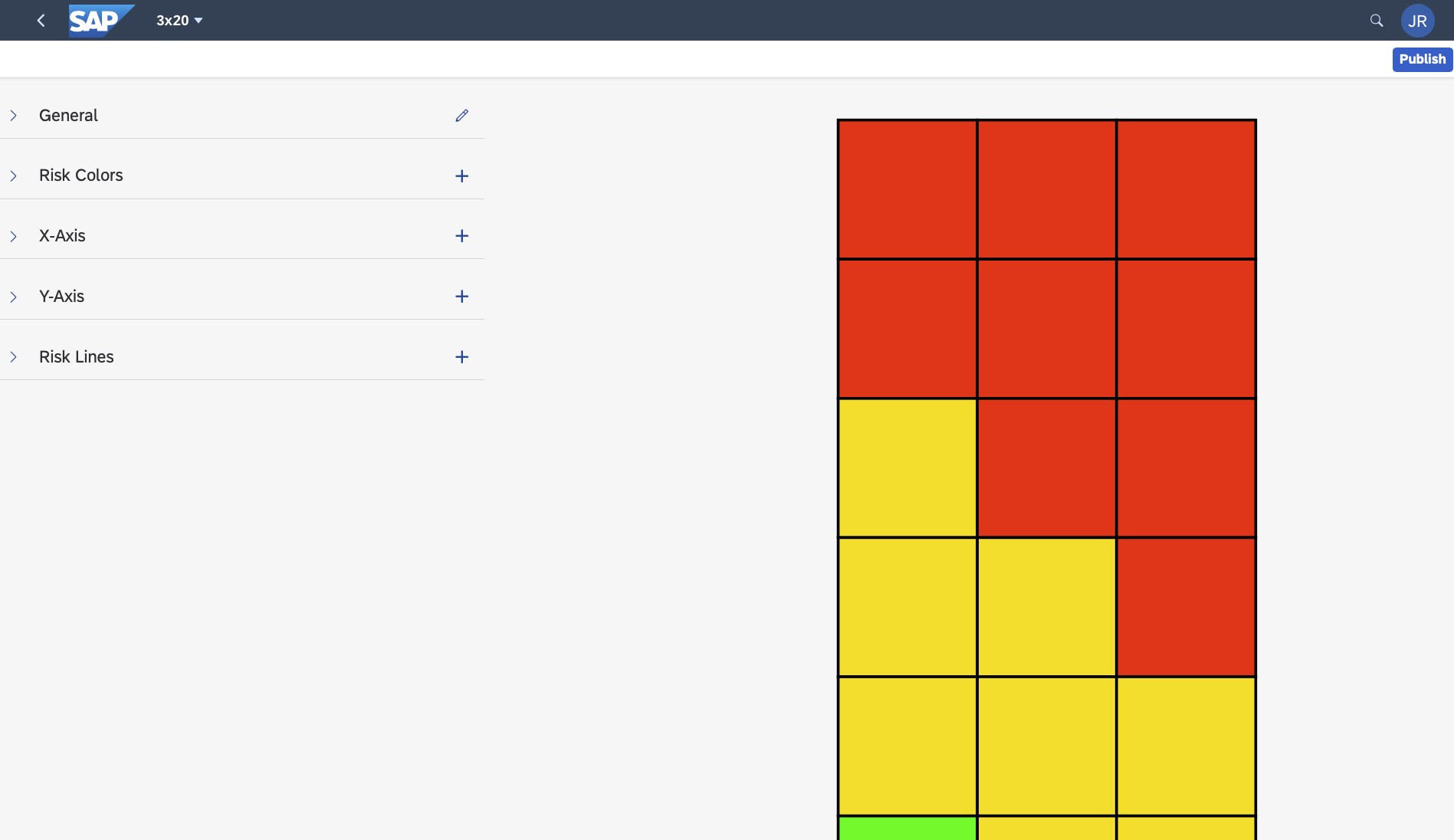
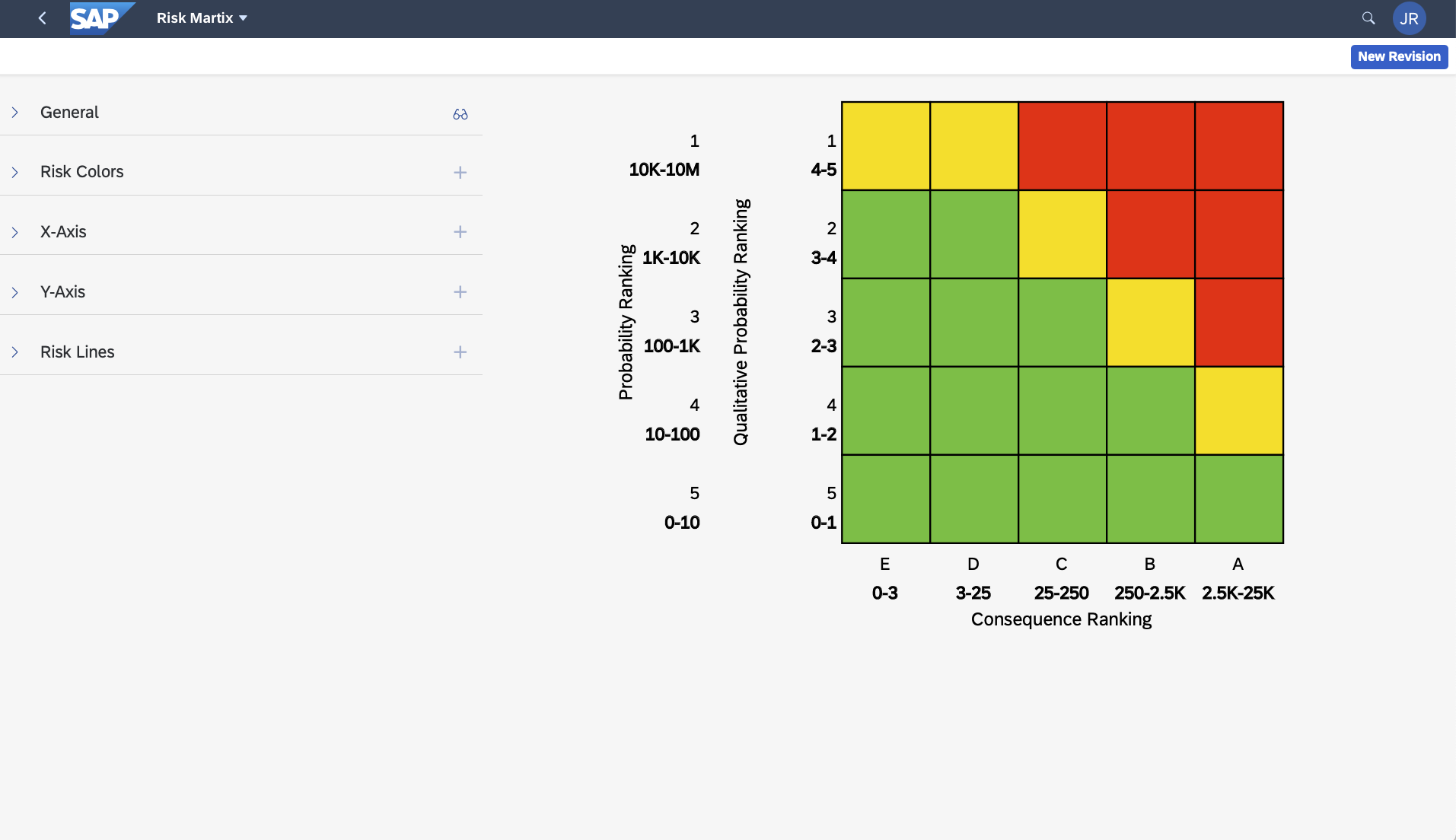
RBI+ Matrix Default Configuration
By default, the RBI+ Matrix has the below configuration for Consequence and Probability, but can be changed without coding to meet the customer needs.
Consequence - The Consequence of Failure is at the component level. The consequence of failure for each component will independently analyze the consequences of a flammable event, a toxic event, a thermal health hazard event, an environmental event, and a business event, based on the NFPA rating. The rough steps are:
(tap to enlarge)
Determine the NFPA fluid rating
Calculate the Hazard and Release Effect
Determine Mass and Release Rate
(tap to enlarge)
Probability - The Probability is based on a Damage Factor approach per API 581 3rd for Age and Non-Age related Mechanism.
(tap to enlarge)
Matrix - The result of the Consequence and Probability can be mapped into a Matrix like this. In this case, the yellow is the inspectable risk range, green is continue to monitor with desktop studies for internals, and red is MOC.
NOTE: This is a sample configuration, customers can change to meet their internal requirements.
